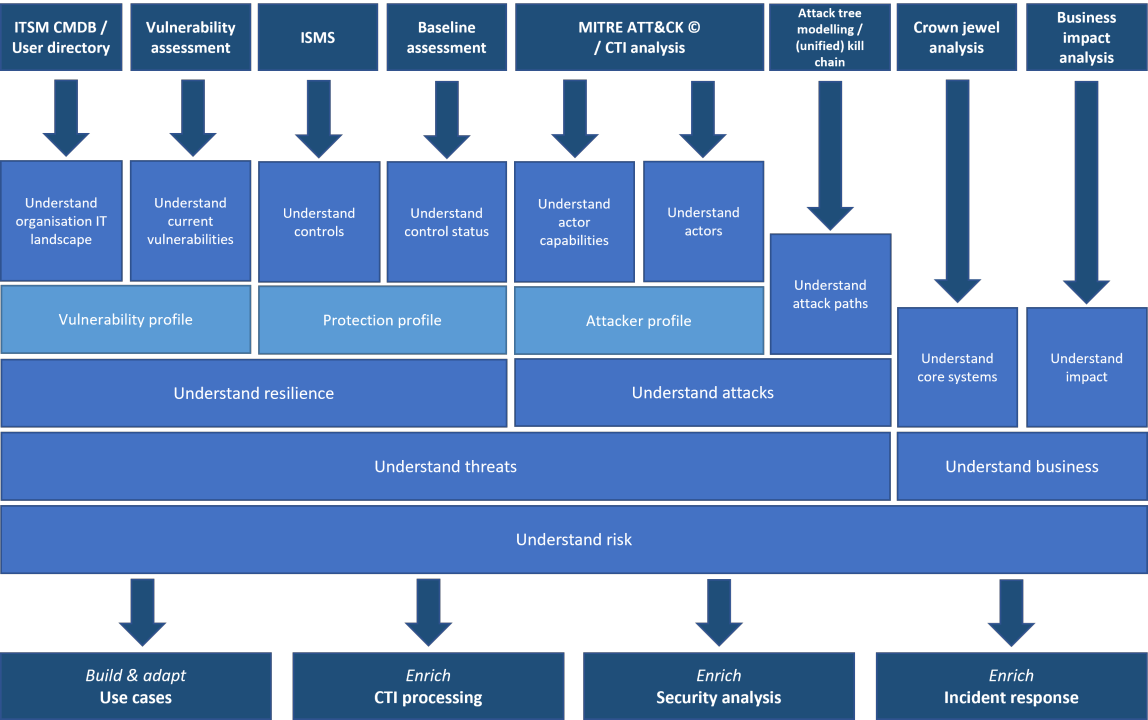
Understanding cyber threats is crucial in today’s digital age. Cyber threat modeling is a key tool in incident response.
In the world of cybersecurity, threats constantly evolve. Cyber threat modeling helps identify, assess, and prioritize these threats. This process aids in creating effective incident response strategies. By anticipating potential attacks, organizations can prepare and protect their data. This blog post delves into the significance of cyber threat modeling.
It explores how this approach enhances incident response efforts. You’ll learn about its benefits and practical applications. Stay tuned to understand how to safeguard your digital assets.

Credit: papers.govtech.com
Introduction To Cyber Threat Modeling
Cyber threat modeling is a structured approach to identify potential threats. It helps security teams understand and respond to cyber attacks effectively. By anticipating threats, organizations can prepare defenses and reduce risks.
Importance In Incident Response
Cyber threat modeling plays a crucial role in incident response. It enables teams to predict and prepare for cyber attacks. This preparation leads to faster and more effective responses.
- Identifies potential vulnerabilities: Threat modeling uncovers weaknesses in systems.
- Improves response time: Knowing potential threats helps in quick action.
- Enhances defense mechanisms: It guides the implementation of robust security measures.
Incorporating threat modeling into incident response plans ensures a proactive security posture. It helps in minimizing damage and recovery time.
Key Concepts
Several key concepts form the foundation of cyber threat modeling:
| Concept | Description |
|---|---|
| Assets | Items of value that need protection, such as data, devices, and networks. |
| Threat Actors | Entities that pose threats, including hackers, insiders, and nation-states. |
| Attack Vectors | Paths or methods used by attackers to exploit vulnerabilities. |
| Mitigations | Actions taken to reduce or eliminate risks from threats. |
Understanding these concepts is essential for effective cyber threat modeling. They help in creating detailed threat scenarios and defense strategies.
By focusing on assets, threat actors, attack vectors, and mitigations, security teams can build a comprehensive threat model. This model guides the incident response efforts, making them more targeted and efficient.
Credit: www.cynet.com
Identifying Threat Actors
In the world of cyber security, identifying threat actors is a crucial step. Knowing who might attack helps in planning effective defenses. This article will explore the different types of threat actors and their motivations.
Types Of Threat Actors
There are various types of threat actors in cyber security. Each has unique methods and goals. Understanding these can help in preparing better defenses.
Hacktivists: These individuals or groups use hacking to promote political ends. They often aim to cause disruption or make a statement.
Cyber Criminals: These actors seek financial gain. They use malware, phishing, and other methods to steal money or data.
Insiders: These threat actors are often employees or associates. They have access to sensitive information and may misuse it.
Nation-State Actors: These are government-backed groups. They aim to gather intelligence or disrupt other nations’ activities.
Script Kiddies: These are inexperienced hackers. They use existing tools and scripts to cause minor disruptions.
Motivations And Goals
Understanding what drives threat actors is essential. Their motivations and goals can vary widely.
Financial Gain: Cyber criminals often seek money. They may steal credit card information or demand ransoms.
Political Agenda: Hacktivists and nation-state actors often have political goals. They might want to influence public opinion or disrupt government operations.
Personal Revenge: Insiders may act out of personal grievances. They might want to harm their employer or a colleague.
Intellectual Challenge: Some hackers are motivated by the challenge. They hack systems to prove their skills.
Espionage: Nation-state actors often engage in espionage. They seek to gather intelligence on other countries or corporations.
Mapping Attack Vectors
Mapping attack vectors is crucial in cyber threat modeling. It helps identify potential paths attackers may use to exploit systems. Understanding these pathways strengthens incident response strategies. Let’s dive deeper into common attack vectors and vector analysis techniques.
Common Attack Vectors
Attackers often exploit several common attack vectors. Phishing is a frequent method. It uses deceptive emails to trick users into revealing sensitive information. Malware is another major threat. It includes viruses, ransomware, and spyware. These malicious software programs can damage or steal data.
Weak passwords also pose significant risks. They are easy targets for brute force attacks. Insider threats come from employees or former staff. They may misuse access to company systems. Network vulnerabilities, like unpatched software, present another vector. Attackers exploit these to infiltrate networks.
Vector Analysis Techniques
Analyzing attack vectors requires specific techniques. Threat intelligence gathering is essential. It involves collecting data on potential threats. This helps predict and prevent attacks. Penetration testing is another technique. It simulates attacks to identify weaknesses.
Behavioral analysis examines user and system behavior. It detects anomalies that may indicate an attack. Risk assessment evaluates the potential impact of different attack vectors. This helps prioritize security efforts. Lastly, using security information and event management (SIEM) tools is effective. They aggregate and analyze data to detect threats in real-time.
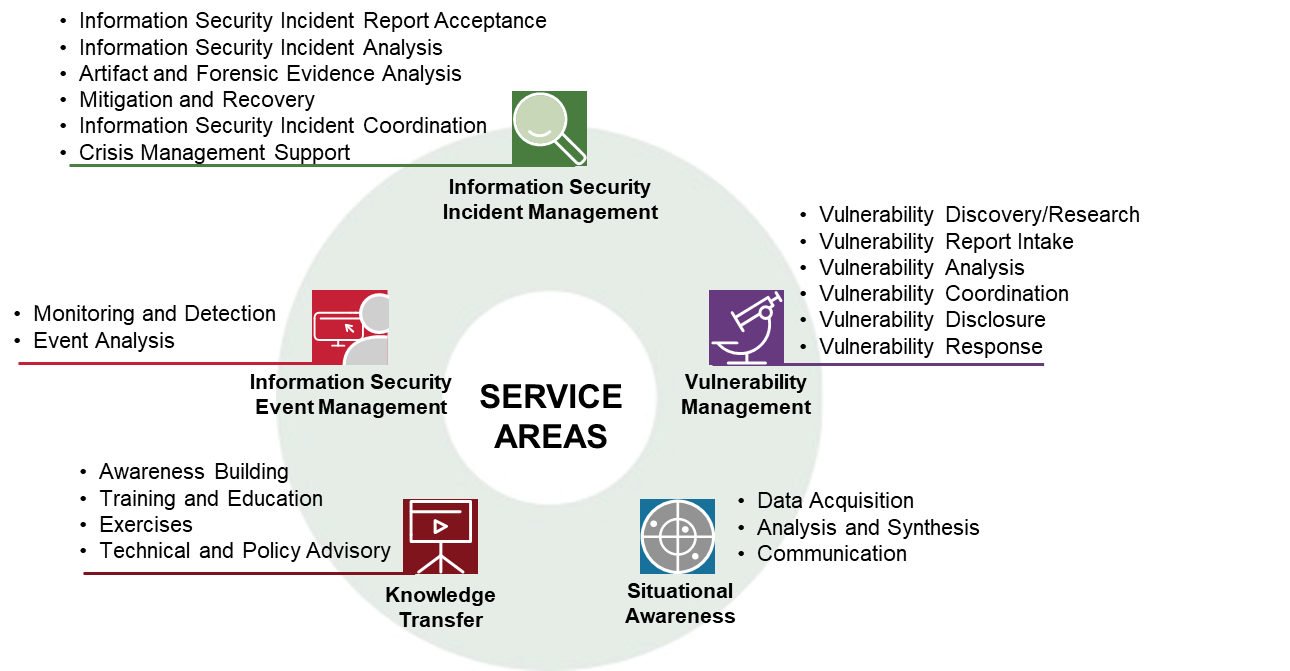
Credit: www.first.org
Assessing Vulnerabilities
Assessing vulnerabilities is a critical step in cyber threat modeling. Understanding potential weaknesses helps in creating effective incident response plans. This ensures the security of your systems and data.
Vulnerability Identification
Identifying vulnerabilities involves a detailed examination of your systems. This can be done through:
- Regular security audits
- Penetration testing
- Code reviews
Security audits help uncover hidden flaws. Penetration testing simulates cyber attacks. Code reviews check for programming errors. All these methods aim to find weak spots before attackers do.
Impact Assessment
Once vulnerabilities are identified, it is vital to assess their impact. This involves understanding the potential consequences of each vulnerability. Key factors to consider include:
| Factor | Description |
|---|---|
| Data Sensitivity | How sensitive is the data at risk? |
| System Criticality | How critical is the affected system? |
| Exploitability | How easy is it to exploit the vulnerability? |
Assessing these factors helps prioritize vulnerabilities. It ensures that the most critical issues are addressed first. This step is essential for efficient incident response planning.
Creating Threat Scenarios
Creating threat scenarios is a key part of cyber threat modeling. These scenarios help predict potential cyber attacks and how they might affect your organization. By anticipating threats, you can prepare and respond better.
Scenario Development
Scenario development involves creating detailed descriptions of possible cyber threats. Start by identifying the assets that need protection. Then, think about who might target these assets and why. Consider both internal and external threats. Create realistic scenarios based on past incidents and current threat intelligence.
Each scenario should include the method of attack, the goal of the attacker, and the potential impact on the organization. This helps in understanding the threat landscape better. It also aids in planning effective response strategies.
Simulation Techniques
Simulation techniques bring threat scenarios to life. Use simulations to see how well your team responds to different threats. This practice helps in identifying gaps in your incident response plan. Start with tabletop exercises. These are discussion-based sessions where team members walk through a simulated attack.
Move on to more complex simulations like red teaming. In red teaming, a group of security experts simulates an attack on your organization. This helps in testing your defenses in real-time. Another technique is penetration testing. In this, testers try to find and exploit vulnerabilities in your systems. These simulations provide valuable insights for improving security measures.
Prioritizing Threat Responses
Effective incident response hinges on prioritizing threat responses. This ensures resources are used wisely and threats are mitigated quickly. By focusing on the most critical risks, organizations can minimize damage and recover faster.
Risk Assessment
Risk assessment is the first step in prioritizing threat responses. By evaluating potential threats, organizations can identify which ones pose the most danger.
Key factors to consider:
- Impact: What damage can the threat cause?
- Likelihood: How probable is the threat?
- Detectability: How easily can the threat be detected?
- Response Capability: How prepared is the organization to respond?
Using these factors, organizations can score and rank threats. This helps in deciding which threats need immediate attention.
Response Strategies
Once risks are assessed, response strategies can be developed. These strategies should be tailored to the specific threats.
Common response strategies include:
- Containment: Isolate affected systems to prevent spread.
- Eradication: Remove the threat from the environment.
- Recovery: Restore systems to normal operation.
- Lessons Learned: Analyze the incident to improve future responses.
A well-defined response strategy ensures a quick and effective reaction to threats.
Consider the following table for a clearer understanding:
| Threat | Impact | Likelihood | Response Strategy |
|---|---|---|---|
| Phishing Attack | High | Medium | Containment, Eradication |
| Malware Infection | Medium | High | Containment, Eradication, Recovery |
| Data Breach | High | Low | Containment, Lessons Learned |
By prioritizing threats and developing targeted response strategies, organizations can enhance their incident response efforts.
Integrating With Incident Response
Integrating cyber threat modeling with incident response is essential for effective security management. This approach helps in identifying potential threats and enhances the response strategy. By incorporating threat modeling, teams can anticipate attacks and prepare better defenses. This section will cover how to integrate cyber threat modeling with incident response.
Workflow Integration
Integrating threat modeling into the incident response workflow streamlines processes. Security teams can identify potential threats early and prioritize responses. This proactive approach saves time during an actual incident. Consistent updates to the threat model ensure it remains relevant. Automation tools can assist in keeping the workflow efficient. Teams can simulate various attack scenarios and refine their response strategies.
Collaboration With Teams
Effective collaboration is crucial for integrating threat modeling with incident response. Different teams need to share information and insights regularly. Security, IT, and management teams should work together. Regular meetings and updates can enhance communication. Clear roles and responsibilities help avoid confusion during an incident. Collaborative tools can aid in real-time information sharing.
Training sessions and workshops can improve team coordination. Understanding each team’s strengths and weaknesses is essential. This knowledge can help in assigning tasks during an incident. A united approach ensures a robust defense against cyber threats.
Tools And Techniques
In the world of cyber threat modeling, having the right tools and techniques is essential. These resources help teams identify, assess, and respond to potential threats effectively. Below, we discuss some of the most commonly used software solutions and manual methods in cyber threat modeling.
Software Solutions
Several software solutions streamline the threat modeling process. These tools automate many tasks, making them efficient and reliable.
- Microsoft Threat Modeling Tool: This tool helps visualize potential threats. It creates data flow diagrams to identify vulnerabilities.
- OWASP Threat Dragon: An open-source tool, it focuses on web applications. It assists in creating threat models and visualizing risks.
- IriusRisk: This tool integrates with existing development workflows. It provides automated threat modeling and risk analysis.
These solutions save time and increase accuracy. They are user-friendly and offer detailed reports.
Manual Methods
While software solutions are powerful, manual methods are still valuable. They provide a deeper understanding of potential threats.
- Brainstorming Sessions: Teams gather to discuss potential threats. This method fosters collaboration and creativity.
- Threat Libraries: These are collections of known threats. They help teams identify risks based on past incidents.
- Checklists: Comprehensive lists ensure all potential threats are considered. They serve as a guide during the modeling process.
Manual methods require more effort but offer insights that software tools might miss. They are essential for a thorough threat modeling process.
Continuous Improvement
Continuous improvement is crucial for effective cyber threat modeling. It involves regularly updating models and incorporating feedback loops. This ensures that your incident response remains robust and agile. By focusing on continuous improvement, you can better anticipate and mitigate cyber threats. Let’s explore the key components of continuous improvement in cyber threat modeling.
Feedback Loops
Feedback loops are essential for refining your cyber threat models. They allow you to gather insights from past incidents. This information helps you identify patterns and areas for improvement. Implementing feedback loops involves:
- Collecting data from incident responses
- Analyzing the effectiveness of current models
- Identifying gaps and weaknesses
- Making informed adjustments to models
Regular feedback ensures that your models evolve. It keeps them relevant and effective. This proactive approach helps you stay ahead of emerging threats.
Updating Models
Updating models is a continuous process. Cyber threats evolve, and so should your models. Regular updates ensure that your defenses remain strong. Here are some steps to keep your models up to date:
- Reviewing recent threat intelligence reports
- Incorporating new threat indicators
- Adjusting models based on feedback
- Testing updated models against simulated attacks
By consistently updating your models, you improve your incident response capabilities. It helps you better predict and respond to cyber threats.
Continuous improvement in cyber threat modeling is not optional. It is necessary. By utilizing feedback loops and updating models, you maintain a strong defense against evolving cyber threats.
Case Studies And Examples
Understanding cyber threat modeling in incident response can be challenging. Real-world examples help make the concepts clearer. They show how companies handle cyber threats. Let’s explore some of these cases.
Real-world Applications
Many companies use cyber threat modeling to protect their data. One example is a large financial firm. It faced a sophisticated phishing attack. The attackers used fake emails to steal login information.
The firm used threat modeling to identify the attack’s methods. They tracked how the attackers accessed their systems. They found weaknesses in their email filters. The firm improved these filters and trained their staff. This helped them stop future attacks.
Another example is a healthcare company. They suffered a ransomware attack. Patient data was locked and inaccessible. The company used threat modeling to understand the attack. They mapped out the attacker’s steps. They found the entry point was an outdated software system. The company updated their software and added more security layers. This prevented similar attacks in the future.
Lessons Learned
These case studies offer important lessons. First, early detection is crucial. Identifying an attack quickly can limit the damage. Both companies used threat modeling to find and fix weaknesses.
Second, training employees is key. Many attacks start with human error. Teaching staff about phishing and other threats reduces risks. Both firms invested in staff training and saw positive results.
Third, regular updates to systems and software are essential. Outdated systems are easy targets for attackers. Keeping everything updated closes security gaps. The healthcare company learned this the hard way.
In summary, cyber threat modeling helps companies stay one step ahead. Real-world examples show its importance in incident response. These lessons can guide other organizations in protecting their data.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is Cyber Threat Modeling?
Cyber threat modeling is the process of identifying potential security threats and vulnerabilities. It helps in understanding how attackers might exploit these weaknesses. This proactive approach improves incident response strategies.
Why Is Threat Modeling Important In Incident Response?
Threat modeling is crucial as it helps in identifying and mitigating potential security threats. It enhances the effectiveness of incident response by anticipating possible attack vectors. This leads to quicker and more efficient handling of security incidents.
How Does Threat Modeling Improve Cybersecurity?
Threat modeling enhances cybersecurity by identifying and addressing vulnerabilities before attackers can exploit them. It provides a structured approach to assessing threats, which improves overall security posture. This proactive measure helps in preventing security breaches.
What Are Common Threat Modeling Techniques?
Common threat modeling techniques include STRIDE, PASTA, and DREAD. STRIDE focuses on identifying types of threats like spoofing and tampering. PASTA is a risk-centric approach. DREAD evaluates the severity of threats.
Conclusion
Cyber threat modeling is vital in incident response. It helps identify risks quickly. With clear strategies, teams can act faster during attacks. This reduces damage and ensures safety. Using these models keeps systems secure. Stay updated and practice regularly for best results.
Effective threat modeling makes a big difference. Start integrating it today. Protect your data and systems efficiently.